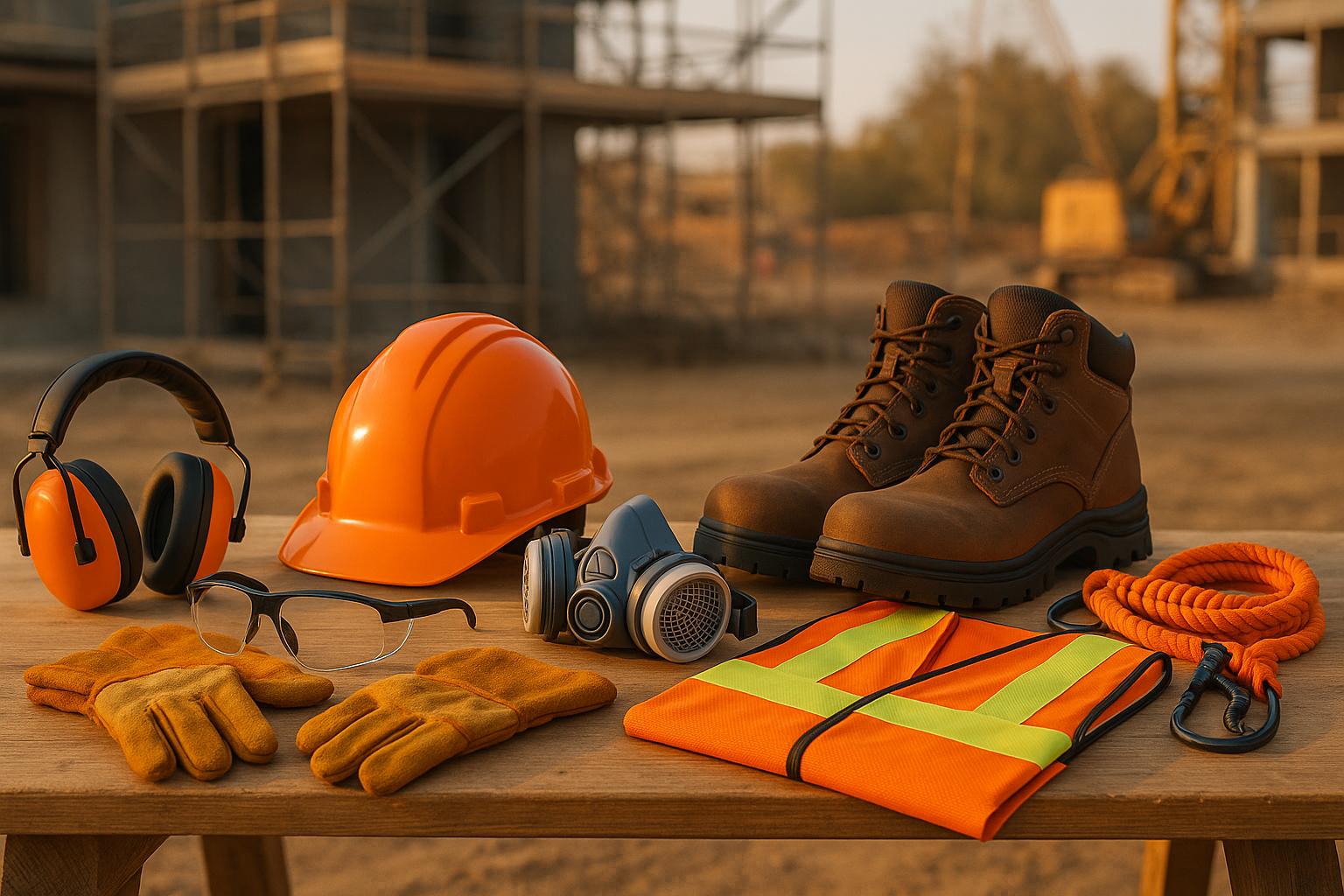
Complete Guide to Construction Safety Equipment
Construction sites are among the most hazardous workplaces in the U.S., with risks like falls, electrocutions, and falling objects. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) serves as the last line of defense, protecting workers from serious injuries and fatalities. Here's what you need to know:
- Key PPE Types: Hard hats, safety harnesses, safety glasses, gloves, and high-visibility clothing.
- Regulations: OSHA mandates hazard assessments, free PPE for workers, and proper training. ANSI sets performance standards for equipment like hard hats (Z89.1) and eyewear (Z87.1).
- Fit and Maintenance: Poorly fitting or damaged PPE can fail when needed most. Routine inspections and proper care are essential.
- Fall Protection: The leading cause of construction fatalities, addressed with gear like harnesses and anchor points.
- Eye, Face, and Hand Protection: Standards ensure safety glasses, gloves, and shields meet specific task requirements.
- Compliance: Employers must maintain records, train workers, and ensure PPE meets certification standards.
The right PPE, combined with proper training and a safety-first mindset, reduces risks, saves lives, and keeps projects running smoothly.
Top 5 Essential PPE Items for Construction | Comfortable & Effective Gear
Types of Construction PPE: Purposes and Standards
Understanding the various types of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) and their associated standards is key for ensuring worker safety on construction sites. Each piece of equipment serves a specific purpose and must meet strict certification requirements to perform effectively in demanding environments.
Hard Hats: Protection and Certification
Hard hats are indispensable on construction sites, shielding workers from falling or flying objects - one of the leading causes of injuries. To meet safety standards, these helmets must comply with ANSI Z89.1, which covers impact resistance, penetration resistance, and electrical insulation.
Electrical protection is classified into three categories:
- Class G (General): Protects against low-voltage conductors up to 2,200 volts.
- Class E (Electrical): Handles higher voltages, up to 20,000 volts.
- Class C (Conductive): Offers no electrical protection but provides enhanced impact resistance.
Modern hard hats come in various designs, such as full brim and cap styles, to improve weather protection and compatibility with other PPE. Features like advanced materials, a 6-point ratchet suspension system, and moisture-wicking liners enhance comfort and reduce strain, encouraging workers to wear them consistently.
Companies can also customize hard hats with logos or branding without compromising safety standards. This not only promotes accountability but also creates a professional appearance on job sites.
Fall Protection: Harnesses and Equipment
Falls remain the leading cause of fatalities in construction, making fall protection critical. OSHA mandates fall protection for workers exposed to heights of 6 feet or more, though some companies enforce stricter measures at lower heights.
Full-body harnesses are designed to distribute fall forces across the chest, pelvis, and thighs, minimizing injury risks. These harnesses must align with ANSI Z359 standards, which outline requirements for strength, hardware, and labeling.
Key components of fall protection systems include:
- D-rings: Positioned on the dorsal, front, or side areas for fall arrest, controlled descent, and work positioning.
- Lanyards: Shock-absorbing lanyards reduce the force of a fall by connecting the harness to an anchor point.
- Self-retracting lifelines: Provide mobility while locking automatically in the event of a fall.
Proper anchor points are essential for these systems to work effectively. Anchor points must support at least 5,000 pounds per worker or meet a 2:1 safety factor when designed by a qualified professional. Temporary solutions, like beam clamps and concrete anchors, offer flexibility for sites lacking permanent anchors.
Routine equipment inspections are vital. Workers should check for signs of wear, chemical damage, or defects before each use. Any damaged equipment must be removed from service immediately.
Eye, Face, and Hand Protection
Protecting the eyes, face, and hands is essential in construction, where hazards like flying debris, chemicals, and sharp tools are common. ANSI Z87.1 sets the standards for occupational eye and face protection, covering impact resistance, optical clarity, and coverage.
- Safety Glasses: Provide basic protection against particles and debris. Look for "Z87" for standard impact protection or "Z87+" for high-impact environments.
- Goggles: Offer superior protection in dusty or chemical-heavy environments. Direct ventilation allows airflow, while indirect ventilation shields against chemical splashes.
- Face Shields: Guard against larger flying objects, chemical splashes, and radiant energy from welding or cutting. However, they must be paired with safety glasses or goggles for complete protection.
For hand protection, selecting the right gloves is crucial. ANSI/ISEA 105 standards rate cut resistance from A1 (low) to A9 (high) and evaluate impact resistance for knuckles and fingers. Chemical resistance depends on the glove material:
- Nitrile Gloves: Resist oils and many chemicals while maintaining dexterity.
- Neoprene Gloves: Effective against acids and caustics.
- PVC Gloves: Provide excellent chemical resistance but are less flexible.
Leather gloves are favored for general construction due to their durability and abrasion resistance, though they lack chemical protection and can pose risks in electrical work by retaining moisture.
Certification and Compliance
Ensuring PPE compliance requires checking for proper certification marks directly on the equipment. Third-party certifications, such as the UL Mark, verify that products meet safety standards through independent testing and annual evaluations.
"In third-party certification, products are tested against safety standards by an independent, accredited organization without bias, and products are inspected and tested annually to evaluate continued compliance. Therefore, third-party certification inspires stakeholders' trust and confidence that the PPE complies with applicable safety requirements."
– UL Solutions
Employers and workers can verify certification through tools like UL Product iQ®, which provides information on PPE compliance across various categories, including protective clothing, footwear, and headgear.
Understanding these PPE types and their standards is the foundation for making informed safety decisions. The next step involves selecting the right equipment for specific tasks and hazards on the job site.
How to Choose the Right PPE for Construction Tasks
Selecting the right personal protective equipment (PPE) starts with understanding the specific risks of each task and matching them with gear that meets safety standards and provides reliable protection for workers. This process begins with a careful evaluation of the hazards involved.
Conducting Hazard Assessments
The first step in choosing PPE is conducting a thorough hazard assessment. According to OSHA, these assessments are mandatory and help determine the necessary protective equipment for specific tasks. They form the backbone of PPE selection, ensuring that workers are adequately protected.
Each task in construction comes with its own set of risks. For instance, welding involves hazards like intense light, flying sparks, and hot metal, which can lead to eye injuries. Electrical work, on the other hand, poses dangers such as electric shock, arc flashes, and burns. Painting jobs often expose workers to chemicals and respiratory risks. Using a checklist that addresses potential risks to the eyes, face, head, and hands can streamline this process.
The work environment also plays a critical role in hazard evaluations. Indoor sites, high-rise projects, and underground workspaces each present unique challenges. These might include confined spaces, poor visibility, falling objects, or environmental exposure. Employers are required to document these assessments in writing to maintain consistency and facilitate compliance audits.
Key Factors in PPE Selection
Once hazards are identified, the focus shifts to selecting PPE that fits well and offers appropriate protection. OSHA’s updated rule, effective January 13, 2025, emphasizes the importance of properly fitting PPE, aligning construction standards with general industry regulations under 29 CFR 1926.95(c). Ill-fitting equipment can reduce effectiveness, fail to protect, or even pose additional risks.
Compatibility is another essential factor. PPE items like hard hats should work seamlessly with other protective gear such as safety glasses, ear protection, and respirators to prevent gaps in protection. Worker comfort should also be considered to ensure consistent use. Durable materials are crucial, as they must withstand hazards like abrasion, chemicals, extreme temperatures, and impacts. For example, carbon fiber hard hats offer excellent impact resistance while being lighter, reducing neck strain during long shifts.
Environmental conditions and task-specific needs also influence PPE choices. High-visibility clothing may require adjustments based on lighting, traffic levels, or weather, while tasks demanding precision might call for thinner gloves to maintain dexterity. In contrast, heavy-duty jobs might prioritize gloves with maximum strength and protection.
After addressing fit and compatibility, it’s vital to confirm that the equipment meets required certifications.
Understanding Product Certifications and Labels
Most PPE must meet ANSI standards, as required by OSHA. Understanding certification markings is key to selecting compliant gear. For example, eye and face protection should meet ANSI Z87.1 standards and display permanent markings confirming compliance.
OSHA’s guidelines for construction PPE are detailed in 29 CFR 1926, particularly Subpart E, which covers Personal Protective and Life Saving Equipment. This includes sections like 1926.95 (general criteria), 1926.100 (head protection), and 1926.102 (eye and face protection). Product labels often indicate the level of protection offered. For example, cut-resistant gloves carry ANSI/ISEA 105 ratings (A1 to A9) to show their resistance level. Additional markings might specify impact protection for knuckles and fingers, and chemical resistance ratings help identify suitable materials for handling hazardous substances.
Verification tools, such as the UL Product iQ® database, are invaluable for confirming that PPE meets required standards, helping to avoid counterfeit or subpar equipment.
sbb-itb-fe3cfb1
PPE Use, Maintenance, and Inspection
The reliability of PPE depends heavily on correct usage and consistent upkeep.
Training Workers in PPE Use
Employers are required to train workers on how to properly care for, maintain, and dispose of PPE. This training helps ensure employees know how to use and handle their equipment safely and effectively.
Inspection and Maintenance Protocols
Routine inspections of PPE are essential. They help extend the equipment's lifespan, keep replacement costs down, and ensure the gear remains effective. Assigning clear responsibilities ensures these protocols are followed consistently.
Employer and Employee Responsibilities
Employees are responsible for keeping their PPE clean and in working condition. On the other hand, employers must provide the necessary training and clear guidelines to support workers in maintaining their equipment properly.
Building a Compliance-Focused Workplace Safety Culture
Creating a workplace where safety is a top priority goes beyond simply having the right tools and equipment. It’s about fostering a mindset where every employee - from workers to supervisors and managers - sees compliance with personal protective equipment (PPE) rules as a core part of daily operations. When safety becomes second nature, it benefits not only worker well-being but also productivity, morale, and even business performance.
Steps to Ensure Compliance with OSHA Regulations
Develop a detailed PPE program that spells out your safety requirements, including regular audits and corrective actions for non-compliance. This document should clearly outline what PPE is needed for specific tasks, how to use and maintain it, and the consequences of failing to follow the rules. Provide every worker with a copy and ensure they fully understand what’s expected.
Keep thorough records of training, inspections, and incidents for at least five years. OSHA inspectors will want to see evidence that safety is a proactive effort, not just a response to issues as they arise.
Perform regular safety audits to spot weaknesses in your PPE program. Weekly job site inspections can help identify whether workers are using their gear correctly - like wearing hard hats properly or securing safety harnesses. Document any issues and address them promptly to prevent minor oversights from turning into serious violations.
Stay informed about regulation updates. OSHA standards change over time, which can impact your PPE requirements. Subscribe to updates, attend industry safety events, and consult experts who specialize in your field. What worked last year may no longer meet compliance standards today.
Getting Worker Buy-In for PPE Use
Make comfort a priority. Workers are less likely to wear PPE if it feels uncomfortable, restrictive, or overly hot. Invest in well-fitting, high-quality gear that allows for ease of movement. When equipment feels good to wear, compliance improves naturally.
Involve workers in the selection process. Allow employees to test different brands and styles of PPE before making large purchases. Giving them a say in what they’ll be using encourages a sense of ownership and commitment while helping you identify the best options for your team’s needs.
Ensure PPE is always accessible. Place equipment stations in convenient spots around job sites and keep them stocked with essentials like gloves and safety glasses. When gear is easy to grab, there’s less room for excuses.
Recognize and reward safe behavior. Publicly acknowledge workers who consistently follow safety protocols or assist others in staying compliant. Whether it’s a shoutout during a meeting or a small bonus for accident-free periods, these rewards reinforce the importance of safety.
Set the example at every level. Supervisors and managers must wear PPE whenever they’re on-site. If leadership cuts corners on safety, workers are likely to follow suit. Modeling good practices from the top down promotes accountability across the board.
Adding PPE Policies to Safety Programs
Incorporate PPE into daily toolbox talks. Start each shift by reviewing the safety gear required for the tasks ahead. This not only sets clear expectations but also provides an opportunity for workers to ask questions or flag equipment concerns.
Integrate PPE into broader safety processes. Rather than treating PPE as a separate requirement, make it an essential part of your overall safety protocols. This helps workers see how PPE contributes to a safer work environment and reinforces the importance of using and maintaining equipment properly.
Establish clear consequences for non-compliance. First-time violations might result in additional training, while repeated offenses could lead to more serious actions like suspension or termination. Consistently enforce these rules across all levels of the workforce.
Emphasize safety in job descriptions and hiring practices. From the start, new hires should understand that PPE compliance is non-negotiable. Include safety requirements in job postings, employment contracts, and onboarding programs to set the tone from day one.
Regularly review and update policies. Use incident reports, near-miss events, and changes in work conditions to refine your PPE program. As your company takes on new projects or environments, evolving policies ensure they remain effective and relevant.
Conclusion: Improving Construction Safety with the Right PPE
The right construction safety equipment does more than just meet regulations - it saves lives and supports efficient, thriving businesses. Each properly worn hard hat, harness, or pair of safety glasses plays a crucial role in ensuring workers return home safely at the end of the day. These core principles guide every decision made on the job site.
While OSHA and ANSI standards set the foundation for safety, effective contractors go beyond the basics. They choose PPE that not only meets safety requirements but also fits well, functions reliably, and is easy for workers to use consistently. Tailoring equipment to specific tasks and hazards creates a safer and more productive environment.
Investing in high-quality PPE pays off in multiple ways. It lowers injury-related costs, reduces insurance premiums, and enhances overall productivity. When safety becomes an ingrained habit rather than an afterthought, projects tend to run more smoothly, and deadlines are easier to meet.
However, even the best PPE is useless if it’s left unused. This is where workplace culture takes center stage. Companies that actively involve workers in selecting equipment, ensure gear is comfortable and accessible, and enforce safety policies consistently see far greater compliance. Leadership that prioritizes and models safe behavior creates a culture where unsafe practices are not tolerated.
Regular training and routine inspections, as mentioned earlier, further strengthen this approach. Damaged hard hats or worn-out harnesses can fail when they’re needed most, turning a false sense of security into a serious hazard. Ongoing maintenance and vigilance are essential to ensure PPE performs as intended.
By combining thoughtful equipment selection, thorough training, consistent policy enforcement, and a commitment to continuous improvement, contractors can effectively manage construction risks. This approach transforms safety incidents from routine occurrences into rare exceptions, making job sites safer for everyone.
Over the years, the construction industry has made impressive progress in worker safety, with PPE playing a vital role in that success. Every worker deserves to go home safely, and a well-executed PPE program ensures they do.
FAQs
How can employers make sure the PPE they provide meets safety standards and is comfortable enough for workers to use consistently?
Employers can make sure personal protective equipment (PPE) is both safe and comfortable by focusing on three key areas: safety standards, proper fit, and usability. PPE should always meet or exceed the requirements set by OSHA and ANSI to ensure workers are well-protected. Beyond compliance, choosing equipment that fits correctly and is tailored to specific tasks can make a big difference in comfort and encourage consistent use.
To tackle discomfort, providing training is essential. Workers need to understand why PPE is important and how to wear it properly. Employers should also seek regular feedback from employees to pinpoint and address any issues with fit or comfort. By balancing safety with wearability, businesses can create a workplace where PPE is not just a requirement but a practical and accepted part of the job.
How can I perform a hazard assessment to choose the right PPE for a construction job?
To select the right personal protective equipment (PPE) for a construction job, start by assessing the workplace for potential hazards. These might include falling objects, sharp tools, loud noise, chemical exposure, or extreme weather conditions. Take the time to evaluate how likely these risks are to occur and how severe their impact could be.
Once you've identified the hazards, prioritize reducing or eliminating them through engineering solutions or improved work practices. If any risks remain, choose PPE that offers the right level of protection for the specific dangers present. Be sure to document your findings, noting the date and the individual responsible for the assessment, to meet safety compliance requirements. As worksite conditions evolve, revisit and update your hazard assessment regularly.
Why are regular training sessions and PPE inspections essential for workplace safety and OSHA compliance?
Regular training and inspections play a key role in keeping workplaces safe and ensuring compliance with OSHA standards. Training equips employees with the know-how to properly use, maintain, and recognize the limits of their personal protective equipment (PPE). This understanding helps minimize accidents, prevent injuries, and address potential risks effectively.
On the other hand, frequent inspections confirm that PPE remains in good working condition. Worn-out or damaged equipment can put safety at risk, making it essential to identify and replace faulty items quickly. By combining thorough training with regular inspections, you create a safer work environment while staying aligned with OSHA requirements.


