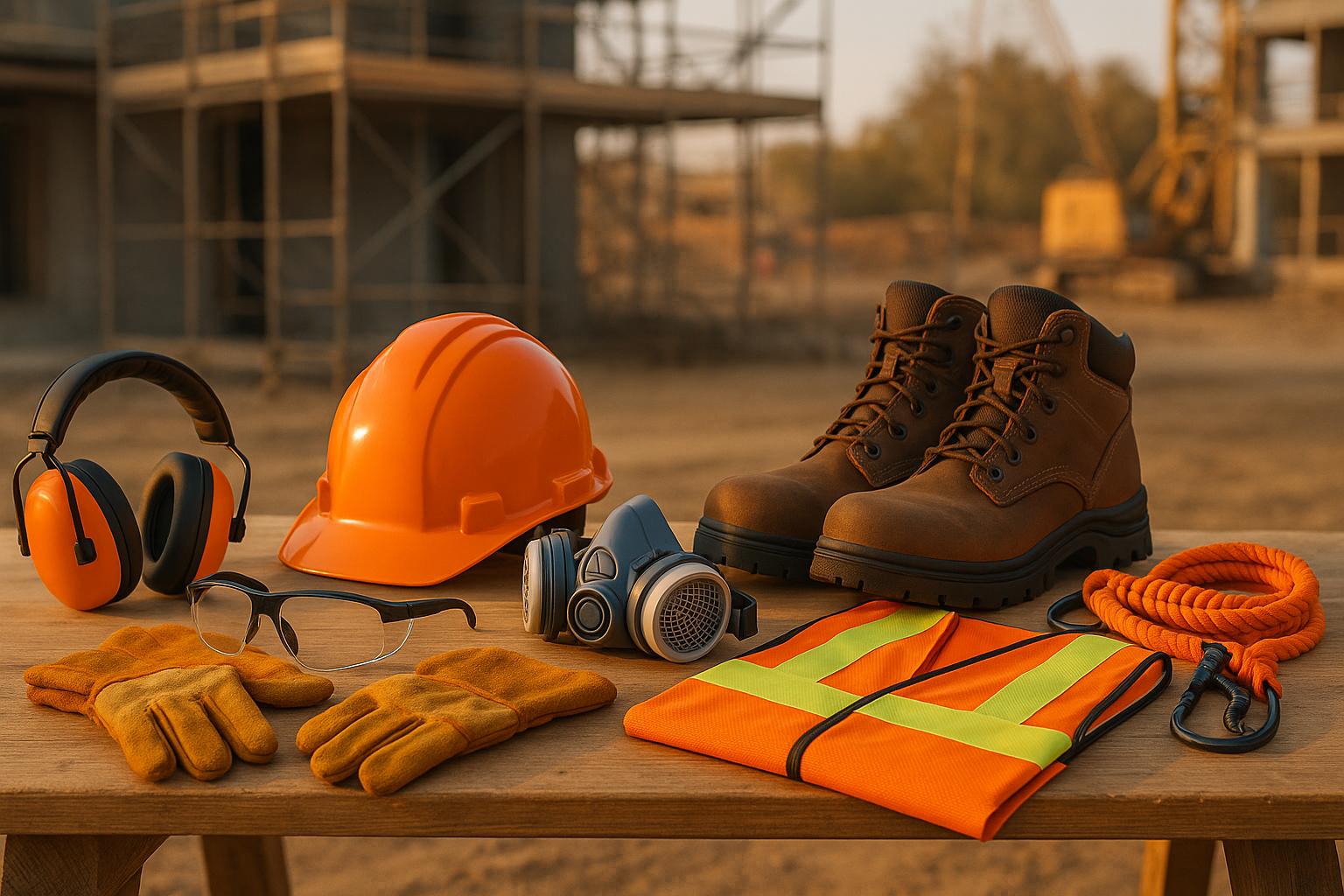
10 Essential PPE Items Every Construction Site Needs
Construction sites are risky environments, but the right personal protective equipment (PPE) minimizes hazards and keeps workers safe. OSHA and ANSI standards mandate that employers provide PPE to protect against risks like falling debris, chemical exposure, and loud noise. Here’s a quick breakdown of the 10 must-have PPE items for every construction site:
- Hard Hats: Protects against falling debris; must meet OSHA 29 CFR 1926.100 standards.
- Safety Glasses: Shields eyes from dust, debris, and chemicals; compliant with ANSI Z87.1.
- Hearing Protection: Reduces noise exposure; devices should fit securely and offer 25–33 dB noise reduction.
- Respirators: Protects lungs from dust, silica, and fumes; must follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910.134.
- Safety Gloves: Defends hands against cuts, chemicals, and impacts; choose gloves rated for specific tasks.
- Steel-Toe Boots: Prevents foot injuries from heavy objects and sharp materials; ASTM F2413-compliant.
- High-Visibility Vests: Enhances visibility in low-light or high-traffic areas; ANSI/ISEA 107-certified.
- Fall Protection Equipment: Includes harnesses and lifelines for work at heights; adheres to OSHA 29 CFR 1926.502.
- Protective Clothing: Shields against chemical splashes, burns, and extreme temperatures; must fit properly.
- Face Shields: Offers full-face protection from flying debris and splashes; ANSI Z87.1-compliant.
Key Takeaway
Proper PPE selection, fit, and maintenance are critical for worker safety. Ensure all equipment meets OSHA/ANSI standards and is comfortable enough for daily use. Regular inspections and training are essential to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
Personal Protective Equipment PPE Construction Safety - Module 7 | OSHA 30 Construction Study Guide
1. Hard Hats
Hard hats are a critical piece of safety gear on construction sites, designed to protect workers from potential dangers like falling debris. Let’s take a closer look at the OSHA standards that ensure their effectiveness.
Compliance with OSHA Standards
To meet federal safety requirements, hard hats used on construction sites must adhere to OSHA standard 29 CFR 1926.100, which specifically addresses head protection, as well as the broader OSHA standard 29 CFR 1926.95, covering general personal protective equipment (PPE) guidelines. A recent update to 29 CFR 1926.95, set to take effect on January 13, 2025, adds a new layer of protection by mandating that all PPE, including hard hats, must properly fit workers in the construction industry. This change underscores the importance of selecting and adjusting PPE correctly to guard against hazards like falling objects while also encouraging workers to follow safety protocols on-site.
2. Safety Glasses and Eye Protection
Right after head protection, keeping your eyes safe is just as critical on construction sites. According to OSHA standards, safety glasses need to be tough, pass impact tests, and fit securely and comfortably. Using lightweight polycarbonate materials, along with scratch-resistant and anti-fog coatings, helps ensure these glasses stay durable while providing clear vision throughout long work shifts. These features work together to protect workers' eyes, adding another layer to the overall safety measures.
3. Hearing Protection
Right after head and eye protection, safeguarding hearing is just as important on construction sites. Noise hazards are a constant threat to workers' hearing, making proper protection essential. However, for hearing protection devices to do their job, they need to fit correctly. Poorly fitting devices not only fail to protect but can also cause discomfort and even lead to ear infections. When protection feels uncomfortable or doesn’t stay secure, the risk of workers not using it properly increases.
A "one-size-fits-all" solution simply doesn’t work when it comes to hearing protection. Employers have a responsibility to provide gear that fits properly and to train workers on how to use, adjust, maintain, and understand the limitations of their equipment. Including workers in the selection process can make a big difference. By trying out different styles and sizes, workers can choose a device that not only provides the necessary protection but is also comfortable enough to wear consistently.
4. Respiratory Protection
Construction workers encounter a range of airborne hazards, including concrete dust, silica, chemical vapors, and asbestos. Respiratory protection acts as a crucial shield, safeguarding workers' lungs from both immediate and long-term health risks.
The lungs alone can’t effectively filter out tiny particles. For example, silica dust consists of microscopic particles that can settle deep in the lungs, increasing the risk of silicosis and even lung cancer over time if proper protection isn’t used.
Choosing the Right Respiratory Protection
Selecting the appropriate respiratory device depends on the specific hazard. Here’s a breakdown of common options and their uses:
- Dust masks and filtering facepiece respirators: These are ideal for tasks like sanding, grinding, or drywall work. Models with N95, N99, or P100 ratings can filter out up to 99.97% of airborne particles.
- Half-face and full-face respirators: Equipped with replaceable cartridges, these offer stronger protection against chemical exposures, paint fumes, and solvents. Cartridges can be tailored to specific hazards, such as organic vapor cartridges for paint or acid gas cartridges for welding.
- Powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs): These are best for extended periods in heavily contaminated environments. They use a battery-powered system to deliver filtered air, reducing breathing effort and providing consistent airflow during demanding tasks.
OSHA/ANSI Compliance
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers to implement respiratory protection programs under its Respiratory Protection Standard (29 CFR 1910.134). When engineering controls can’t sufficiently reduce airborne hazards, these programs become mandatory. Key requirements include:
- Medical evaluations: Ensuring workers are physically able to use respirators.
- Fit testing: Verifying a proper seal between the respirator and the worker’s face.
- Training: Educating workers on correct usage, maintenance, and limitations.
Respirators must carry NIOSH approval markings, which confirm that the equipment has passed rigorous testing for filtration, durability, and breathing resistance. ANSI Z88.2 standards also provide detailed guidance for selecting and maintaining respirators, ensuring employers choose the right protection for specific hazards.
Fit and Comfort
A proper fit is essential for respirators to work effectively. Both quantitative and qualitative tests ensure no contaminated air leaks through. If a respirator doesn’t seal correctly, it allows unfiltered air to bypass the device entirely, compromising safety.
Facial hair can interfere with the seal, even a small amount of stubble. Workers with facial hair should consider positive-pressure respirators, like PAPRs or supplied-air systems, which don’t rely on a tight face seal.
Comfort is another critical factor. Respirators that cause excessive heat, moisture buildup, or pressure points are more likely to be removed or worn improperly. Modern designs address these issues with features like:
- Low-profile exhalation valves to minimize heat and moisture.
- Adjustable head straps for a secure yet comfortable fit.
- Lightweight materials to reduce neck strain during long shifts.
Durability and Material Quality
Durability is just as important as fit, especially in tough construction environments. Respirators must endure impacts, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures while maintaining performance.
High-quality models use multi-layer filters that resist clogging in dusty conditions while remaining breathable. The housing materials are designed to withstand harsh environments without degrading. Replacement schedules for filters and cartridges depend on workplace conditions and manufacturer guidelines. In dusty environments, filters may need daily changes, while chemical cartridges might last longer in less intense exposures. Indicators like increased breathing resistance, visual cues, or noticeable odors signal when replacements are necessary.
5. Safety Gloves
Our hands are essential tools, yet they face daily risks like cuts, punctures, chemical burns, and crushing injuries. Safety gloves are a key line of defense, but choosing the wrong pair can leave workers vulnerable.
The right gloves can significantly reduce injuries. For construction workers, hands are involved in nearly every task - whether it’s handling sharp materials, operating power tools, or working with chemicals. Let’s look at how specific glove types tackle various on-site hazards.
Specific Use Case or Hazard Protection
Different tasks demand specialized gloves. For example, cut-resistant gloves meet ANSI/ISEA standards, with ratings tailored to the severity of potential cuts. These are ideal for handling sharp objects like metal or glass.
Chemical-resistant gloves - made from materials like nitrile, neoprene, or PVC - shield workers from exposure to solvents and cleaning agents. Nitrile gloves are especially effective against oils and petroleum products, making them a go-to for maintenance tasks. Neoprene gloves, on the other hand, are better suited for handling acids and caustics, such as those found in concrete work.
For tasks involving heavy impacts, impact-resistant gloves with padded knuckles and fingers help absorb shocks from hammering, drilling, or lifting. Meanwhile, heat-resistant gloves are critical for high-temperature tasks like welding or torch cutting.
Compliance with OSHA/ANSI Standards
Regulations like OSHA’s Hand Protection Standard (29 CFR 1926.95) require employers to provide hand protection suited to the hazards workers face. This means selecting gloves based on specific risks and ensuring they remain in good condition.
ANSI/ISEA standards provide additional guidance, detailing performance testing for gloves. These standards rate gloves for properties like abrasion, cut, tear, puncture, and impact resistance. Manufacturers typically display these ratings on glove packaging, helping employers choose the right protection for any job.
Durability and Material Quality
Construction sites demand gloves that can endure tough conditions while maintaining their protective qualities. For example, synthetic leather palms offer durability, a solid grip, and resistance to cracking. Genuine leather gloves - crafted from cowhide or goatskin - stand out for their strength and heat resistance, with goatskin providing added flexibility for precision tasks.
Coatings also play a big role. Latex, nitrile, and polyurethane coatings enhance grip and durability. Polyurethane coatings, in particular, are ideal for tasks requiring dexterity or touchscreen use. Double-dipped gloves, treated with two coating layers, provide extra durability by creating a reinforced barrier that extends the glove’s life.
Fit and Comfort
A proper fit isn’t just about comfort - it’s about safety. Oversized gloves can slip or snag on machinery, reducing control and tempting workers to remove them during critical tasks. On the flip side, gloves that are too tight can limit movement, cause hand fatigue, and tear more easily.
To address this, gloves come in various sizes to ensure a snug fit. Modern designs also focus on comfort, incorporating breathable materials, micro-foam coatings for grip and airflow, and moisture-wicking liners to keep hands dry during long shifts.
Cuff design is another important factor. Cuffs should protect the wrist without interfering with work attire. And with digital tools becoming more common on job sites, touchscreen-compatible fingertips are increasingly valuable - allowing workers to use tablets and smartphones without removing their gloves. These features align with broader personal protective equipment (PPE) strategies to keep construction workers safe and efficient.
6. Steel-Toe Boots and Protective Footwear
Foot injuries are a frequent risk on construction sites, making steel-toe and other protective boots a must-have for safety and stability. Every day, construction workers face hazards like falling tools, sharp nails, and jagged metal edges. The right footwear not only shields against these dangers but also provides the comfort and stability needed for navigating uneven terrain during long shifts. Just as hard hats and gloves are essential, choosing the right boots is a key part of staying safe on the job.
Specific Use Case or Hazard Protection
Different worksites call for specific features in protective footwear. Steel-toe boots are the go-to choice for protecting against heavy impacts, making them ideal for general construction, demolition, and working with heavy machinery.
For those working near electrical hazards or metal detectors, composite toe boots are a better option. Made from materials like Kevlar, carbon fiber, or plastic, these boots are lightweight, non-conductive, and won’t trigger security systems.
Electrical hazard (EH)–rated boots are designed with non-conductive soles and heels to reduce the risk of electric shock in dry conditions. Puncture-resistant soles are another critical feature, offering protection from sharp objects like nails and screws while maintaining comfort.
Specialized environments require even more tailored features. Waterproof boots are essential for wet conditions, insulated boots keep feet warm in cold weather, and chemical-resistant boots guard against exposure to hazardous substances like solvents.
Compliance with OSHA/ANSI Standards
OSHA’s Personal Protective Equipment standards (29 CFR 1926.95) mandate that employers provide protective footwear in areas where workers face risks like falling objects, punctures, or electrical hazards. In addition, ASTM standards define how protective footwear should perform. For example, ASTM F2413 sets the requirements for impact resistance, compression protection, metatarsal safety, puncture resistance, and electrical hazard shielding.
Boots that meet these standards are marked with labels showing their protection levels. For instance, a boot compliant with ASTM F2413-18 will have clear markings detailing its performance in areas like impact and electrical safety.
Durability and Material Quality
Construction boots need to stand up to tough conditions while keeping their protective features intact. Full-grain leather is a popular choice for its durability and water resistance, while nubuck offers similar strength with better breathability for hot environments. Synthetic materials are often preferred when lightweight construction, fast drying, or chemical resistance is required.
The construction of the sole also matters. Goodyear welt construction creates a durable bond between the upper and the sole, allowing the boots to be resoled when the tread wears out. For wet environments, direct-attach construction provides a waterproof seal by bonding the sole directly to the upper. Outsole materials vary by need: rubber offers excellent grip and electrical insulation, while polyurethane provides cushioning and resists oil.
Fit and Comfort
A proper fit is just as important as durability. To avoid discomfort and fatigue, boots should leave about a thumb’s width of space between the toes and the front of the boot. They should also accommodate thick work socks and allow for natural foot swelling during long shifts.
Arch support is crucial for reducing strain during extended periods on your feet. Many boots include contoured footbeds or removable insoles for added support, while some feature built-in shanks - made of either metal or composite - for extra stability and puncture resistance.
Moisture management plays a big role in comfort and foot health. Breathable linings, such as those made with Gore-Tex, let moisture escape while keeping water out. Antimicrobial treatments help control odor and bacteria, especially during long hours of wear.
Breaking in boots can take time, depending on the material. Full-grain leather boots often require a longer break-in period, but they tend to mold to the shape of your foot over time. Synthetic options may feel comfortable right out of the box but might not provide the same tailored fit as leather.
Modern boots now come with features like cushioned midsoles, moisture-wicking linings, and ergonomic designs to keep workers safe and comfortable throughout their shifts.
sbb-itb-fe3cfb1
7. High-Visibility Safety Vests
High-visibility safety vests play a critical role on construction sites, especially in low-light or high-traffic situations. They enhance visibility and help ensure workers comply with safety regulations. Alongside hard hats and gloves, these vests are a key part of any comprehensive personal protective equipment (PPE) plan.
Compliance with OSHA/ANSI Standards
OSHA mandates the use of high-visibility clothing in areas with vehicle traffic or moving equipment to protect workers. The ANSI/ISEA 107 standard outlines specific requirements for these vests, including the use of fluorescent colors and retroreflective materials to maximize visibility and keep workers safe in various conditions.
Fit and Comfort
The right fit is essential for both safety and comfort. A vest that's too tight can restrict movement, while one that's too loose may shift and create risks. Most high-visibility vests come with adjustable features like side straps or closures, allowing for a more tailored fit. To ensure the vest fits properly, measure the worker’s chest, waist, and height, keeping in mind that it should comfortably fit over regular work clothing, including extra layers for cold weather. Workers should also test the vest by raising their arms to confirm it stays securely in place during typical tasks.
| Size | Fits Chest Size (inches) | Fits Chest Size (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| S/M | 36-44 | 91-112 |
| L/XL | 44-52 | 112-132 |
| 2XL/3XL | 52-58 | 132-147 |
| 4XL/5XL | 58-64 | 147-163 |
Durability and Material Quality
Durability is just as important as visibility when choosing a safety vest. These vests must endure tough working conditions while maintaining their reflective properties. Lightweight, breathable fabrics like polyester are ideal for hot and humid environments, while insulated or water-resistant options provide extra comfort in cold or wet weather. Regular inspections are crucial to check for wear and tear, ensuring the reflective elements remain intact and the vest continues to fit properly. By prioritizing durability and fit, high-visibility vests contribute significantly to worker safety throughout every shift.
8. Fall Protection Equipment
Fall protection equipment plays a crucial role in keeping workers safe on construction sites. In 2022 alone, falls caused 865 fatalities, with 700 of those resulting from falls at heights - equating to nearly two deaths every day.
"Falls continue to be the leading cause of death in the construction industry." - Jose Herrera, Occupational Safety and Health Specialist and Spanish Instruction Safety Specialist for OSHA
Compliance with OSHA/ANSI Standards
OSHA mandates fall protection for construction workers operating at heights of six feet or more above the ground or lower levels. This rule also applies to work performed over dangerous equipment or machinery, regardless of the height. Given that falls consistently rank as the most frequent OSHA violation, adhering to these standards is not just about meeting regulations - it’s about saving lives.
Employers are required to provide both fall protection systems and training. Training must cover proper usage, inspection, and maintenance of equipment. To ensure accessibility, it must also be delivered in a language workers can understand. Clear communication is key to creating a safe work environment where everyone understands how to protect themselves. Selecting the right fall protection system for the job at hand is equally important.
Specific Use Case or Hazard Protection
Different tasks call for different fall protection solutions. Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) - which include full-body harnesses, anchorage points, lanyards, and Self-Retracting Lifelines (SRLs) - are essential for roof work, scaffolds, ladders, and elevated platforms. SRLs are particularly useful because they provide secure anchoring while allowing workers to move freely.
Other options, such as guardrail systems and safety net systems, offer protection for elevated work areas like overhead platforms, ramps, and walkways. The choice of equipment depends on the specific risks and the type of work being performed.
Fit and Comfort
Meeting safety standards is critical, but so is ensuring the equipment fits properly and is comfortable to wear. A well-fitted harness should feel snug but still allow full movement. Key points to check include the D-ring placement at the center of the back, the chest strap positioned at mid-chest, and shoulder and leg straps without slack.
When selecting harnesses, it’s important to accommodate workers of all sizes, including women. The harness should fit comfortably over standard work clothing and allow workers to perform their tasks without feeling restricted. Comfort is more than a luxury - it ensures workers are more likely to wear their gear consistently.
Durability and Material Quality
The effectiveness of fall protection equipment depends on its durability and the quality of its materials. Workers must inspect their equipment before every shift to check for signs of wear or damage, while a qualified individual should perform a more thorough inspection every six months - or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Look for issues such as loose threads, pulled rivets, burns, cuts, or abrasions. Hardware, including hooks, buckles, and D-rings, should be checked for cracks or breaks. Any damaged equipment must be removed from use immediately to avoid failures in critical moments.
Proper maintenance and storage are also essential for extending the life of fall protection gear. Environmental factors like extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, and UV rays can weaken materials over time. Regular monitoring ensures that the equipment remains reliable and safe for workers on the job.
9. Protective Clothing and Coveralls
Protective clothing and coveralls are essential for maintaining safety on construction sites. They shield workers from various risks and reduce exposure to harmful conditions. To ensure effectiveness, this gear must meet stringent regulatory standards.
Compliance with OSHA Standards
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) introduced an updated rule in December 2024, which takes effect on January 13, 2025. This rule mandates that employers provide properly fitting personal protective equipment (PPE) to their workers. Ensuring that protective clothing is the right size and properly adjusted is key to offering maximum protection without creating new safety concerns.
Fit and Comfort
The effectiveness of PPE heavily depends on how well it fits. Ill-fitting gear can not only reduce protection but also put workers at greater risk. Studies highlight that nearly half of construction workers may either use PPE incorrectly or wear gear that doesn’t fit properly, which jeopardizes their safety.
To address this, contractors should provide a variety of sizes to accommodate diverse body types. Features like elastic waistbands or adjustable straps can further enhance the fit. Additionally, proper fit ensures better thermal insulation by minimizing excessive air gaps between the clothing and the worker's body.
10. Face Shields
Face shields create a transparent barrier that covers the entire face, providing protection against flying debris, chemical splashes, and other dangers. They go beyond the capabilities of standard safety glasses by offering broader coverage for the entire facial area.
Specific Use Case or Hazard Protection
While safety glasses protect the eyes, face shields take it further by safeguarding the eyes, nose, mouth, and overall facial area. They are especially useful for tasks like grinding, where sparks and debris are a concern, as well as concrete cutting, sandblasting, and handling chemicals.
Face shields are particularly effective against splash hazards caused by substances like concrete additives, cleaning solvents, or other chemicals used in construction. Workers performing overhead tasks benefit significantly, as the shield protects against falling particles and liquids that could approach from multiple angles.
Another key advantage is the ability to wear prescription glasses underneath. This feature allows workers to maintain clear vision without compromising on safety, combining practicality with full-face protection.
Compliance with OSHA/ANSI Standards
Face shields must comply with ANSI Z87.1 standards, which ensure they can withstand high-speed impacts while maintaining optical clarity. OSHA mandates that employers evaluate workplace hazards and provide face shields when safety glasses alone are insufficient for protection.
Importantly, face shields are considered secondary protection. They should always be paired with safety glasses, as shields alone may not block smaller, high-speed particles that could enter from the sides. This dual-layer approach ensures maximum safety on the job.
Durability and Material Quality
Modern face shields are made from polycarbonate materials, which are resistant to scratches, fogging, and chemical damage. These shields maintain optical clarity even after exposure to dust and routine cleaning. Typically, the material thickness ranges from 0.04 to 0.06 inches, offering a balance between durability and visibility.
Professional-grade shields often feature anti-fog coatings, preventing condensation from obstructing vision during strenuous activities. Additionally, scratch-resistant treatments help extend the lifespan of the shield, keeping the view clear even in harsh environments.
Fit and Comfort
An adjustable headband with cushioned forehead pads ensures a secure fit and even weight distribution, making it comfortable for extended use.
Proper fitting is essential. The shield should sit about 2 to 3 inches away from the face, providing ventilation while still offering protection. It should extend below the chin and wrap around the sides of the face, ensuring full coverage without limiting head movement or peripheral vision. This design ensures workers stay protected and comfortable throughout their tasks.
PPE Comparison Table
Choosing the right PPE for your construction site means finding gear that prioritizes safety, comfort, and functionality. Below is a detailed comparison of common PPE categories, highlighting compliance standards, material quality, and design features. This table serves as a practical guide to help you select the most effective equipment for your needs.
| PPE Item | ANSI/OSHA Standards | Material Quality | Weight/Comfort | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Hats | ANSI Z89.1 Type 1 Class C | HDPE with a suspension system | 12–16 oz | 6-point ratchet suspension, moisture-wicking liner, effective impact distribution |
| Safety Glasses | ANSI Z87.1 | Polycarbonate shatterproof lenses | 1–2 oz | UV protection, anti-fog coating, wrap-around design |
| Hearing Protection | ANSI S3.19, OSHA 29 CFR 1926.95 | Foam, silicone, or polymer materials | 0.5–8 oz | Noise reduction rating of 25–33 dB, secure and comfortable seal |
| Respirators | NIOSH 42 CFR 84 | N95/P100 filter media with silicone seals | 2–12 oz | 95–99.97% filtration efficiency, adjustable straps, valve options available |
| Safety Gloves | ANSI/ISEA 105 | Leather, nitrile, and cut-resistant fibers | 2–6 oz per pair | Various cut resistance levels, enhanced grip, breathable design |
| Steel-Toe Boots | ASTM F2413 | Leather/synthetic upper with steel/composite toe | 2–4 lbs per pair | Impact-resistant, puncture-resistant sole, electrical hazard protection |
| High-Vis Vests | ANSI/ISEA 107 Class 2/3 | Durable polyester mesh with reflective tape | 4–8 oz | 360° visibility, moisture-wicking properties, customizable branding options |
| Fall Protection | ANSI Z359, OSHA 29 CFR 1926.502 | Nylon webbing with aluminum hardware | 3–8 lbs | High tensile strength (up to 5,000 lbs), shock-absorbing lanyard, secure D-ring attachment |
| Protective Clothing | ANSI/ISEA 113 | Flame-resistant cotton and arc-rated materials | 1–3 lbs per garment | Arc ratings of 8–40 cal/cm², breathable fabric, reinforced stress points |
| Face Shields | ANSI Z87.1 | Polycarbonate with 0.04–0.06-inch thickness | 4–8 oz | Anti-fog coating, scratch resistance, 2–3 inches of face clearance |
To ensure safety and reliability, PPE must comply with ANSI and OSHA standards, such as ANSI Z89.1 for hard hats and ANSI Z87.1 for safety glasses. These standards guarantee essential features like impact resistance and optical clarity.
Durable materials, such as HDPE in hard hats or polycarbonate in safety glasses, play a critical role in providing long-lasting protection. However, comfort is just as important. Features like moisture-wicking liners, adjustable straps, and lightweight designs encourage workers to wear PPE consistently, improving overall safety compliance.
When comparing options, focus on long-term durability and performance rather than just the upfront cost. Investing in well-made PPE can reduce replacement frequency, saving money over time. This table emphasizes the importance of selecting the right gear as part of a broader commitment to workplace safety.
Conclusion
Picking the right PPE for your construction site starts with understanding the specific hazards workers face and choosing gear that directly addresses those risks. The ten PPE essentials covered here lay the groundwork for a strong safety program that protects your team.
Once you've identified the right equipment, make sure it meets established safety standards. The standards and table provided in this guide can help you navigate the selection process with confidence.
The comparison table also emphasizes the importance of choosing PPE made with quality materials and designed for comfort. Comfortable gear is more likely to be worn consistently, which is key to maintaining safety on-site.
Remember, proper fit is just as important as the gear itself. Make sure every worker has PPE that fits correctly and can be adjusted as needed.
Lastly, don’t overlook maintenance - inspect and replace PPE regularly to keep your safety program running at its best.
FAQs
How can I make sure PPE fits properly and protects all workers on a construction site?
Ensuring personal protective equipment (PPE) fits well is essential for both safety and comfort. Properly fitting PPE - like hard hats, gloves, goggles, safety boots, and harnesses - helps workers stay protected while reducing risks. Ill-fitting equipment can compromise its effectiveness, increase safety hazards, and even discourage employees from wearing it altogether.
Employers should adhere to OSHA's guidelines, which emphasize that PPE must fit correctly and meet established safety standards. Regular fit checks, offering various sizes, and providing thorough training on proper usage are key steps to ensure workers remain safe and comfortable on the job.
What should you consider when choosing PPE for specific tasks or hazards on a construction site?
Selecting the right personal protective equipment (PPE) for a construction site is crucial for keeping workers safe and meeting safety regulations. Start with a hazard assessment to identify potential risks like falling debris, chemical exposure, or excessive noise. Once you understand the dangers, choose PPE that specifically addresses those risks. Make sure all equipment complies with OSHA and ANSI standards to meet safety requirements.
Think about the work environment too. For example, outdoor construction sites often call for high-visibility vests, while jobs involving heavy machinery might require steel-toe boots. Don’t overlook fit and comfort - gear that fits poorly can discourage workers from wearing it and create additional safety hazards. To make the process more effective, involve workers in selecting PPE. Their input ensures the gear is practical and meets the demands of their daily tasks.
How often should personal protective equipment (PPE) be inspected and replaced on a construction site?
Before using any personal protective equipment (PPE), it's crucial to inspect it thoroughly to ensure it's in proper working condition. Check for visible damage like tears, cracks, discoloration, or excessive wear. If anything seems compromised, replace the item right away - no exceptions.
Some PPE, like hard hats or respirator filters, comes with a recommended lifespan or expiration date. Always stick to the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry standards to know when it’s time for a replacement. Beyond individual checks, companies should make it a priority to carry out annual PPE reviews. These reviews ensure that all equipment meets safety regulations and aligns with the specific needs of the worksite.


